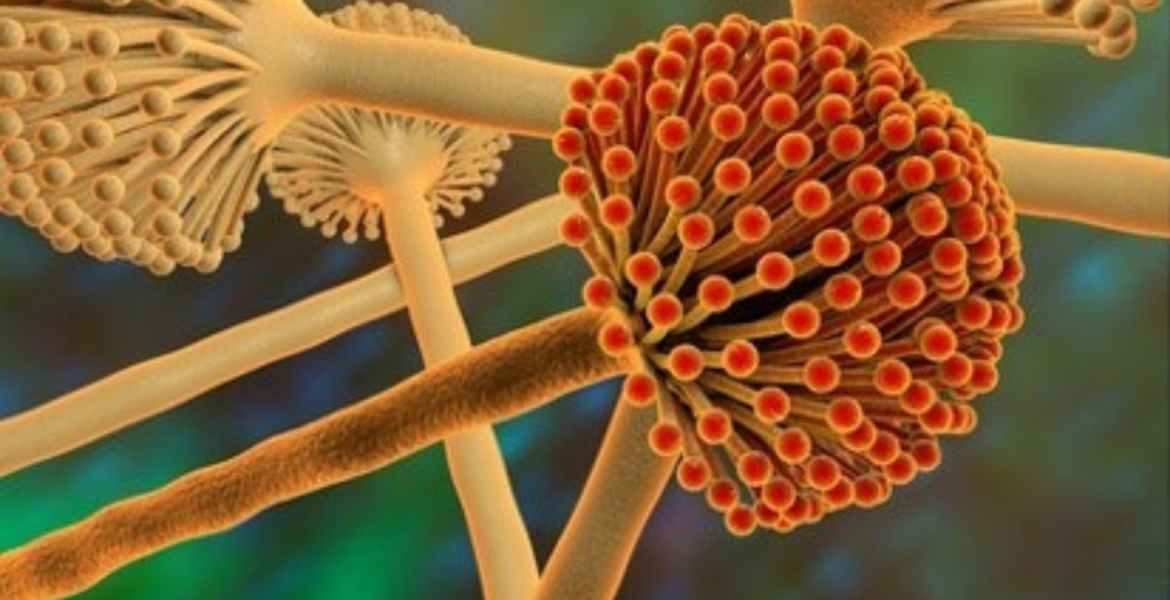
Mold is found in damp building materials where it often appears like stains and comes in a variety of colours. A must smell is an indication of microbial growth even when there is no visible growth. If mold is allowed to grow in homes or offices it can contribute to poor indoor air quality.
Causes
Molds cause biodegradation of natural materials, which can be unwanted when it becomes food spoilage or damage to property. They also play important roles in biotechnology and food science in the production of various foods, beverages, antibiotics, pharmaceuticals and enzymes. Some diseases of animals and humans can be caused by certain molds: disease may result from allergic sensitivity to mold spores, from growth of pathogenic molds within the body, or from the effects of ingested or inhaled toxic compounds (mycotoxins) produced by molds.
Although molds can grow on dead organic matter everywhere in nature, their presence is visible to the unaided eye only when they form large colonies. In artificial environments such as buildings, humidity and temperature are often stable enough to foster the growth of mold colonies, commonly seen as a downy or furry coating growing on food or other surfaces.
Few molds can begin growing at temperatures of 4 °C (39 °F) or below, so food is typically refrigerated at this temperature. When conditions do not enable growth to take place, molds may remain alive in a dormant state depending on the species, within a large range of temperatures. The many different mold species vary enormously in their tolerance to temperature and humidity extremes. Certain molds can survive harsh conditions such as the snow-covered soils of Antarctica, refrigeration, highly acidic solvents, anti-bacterial soap and even petroleum products such as jet fuel.
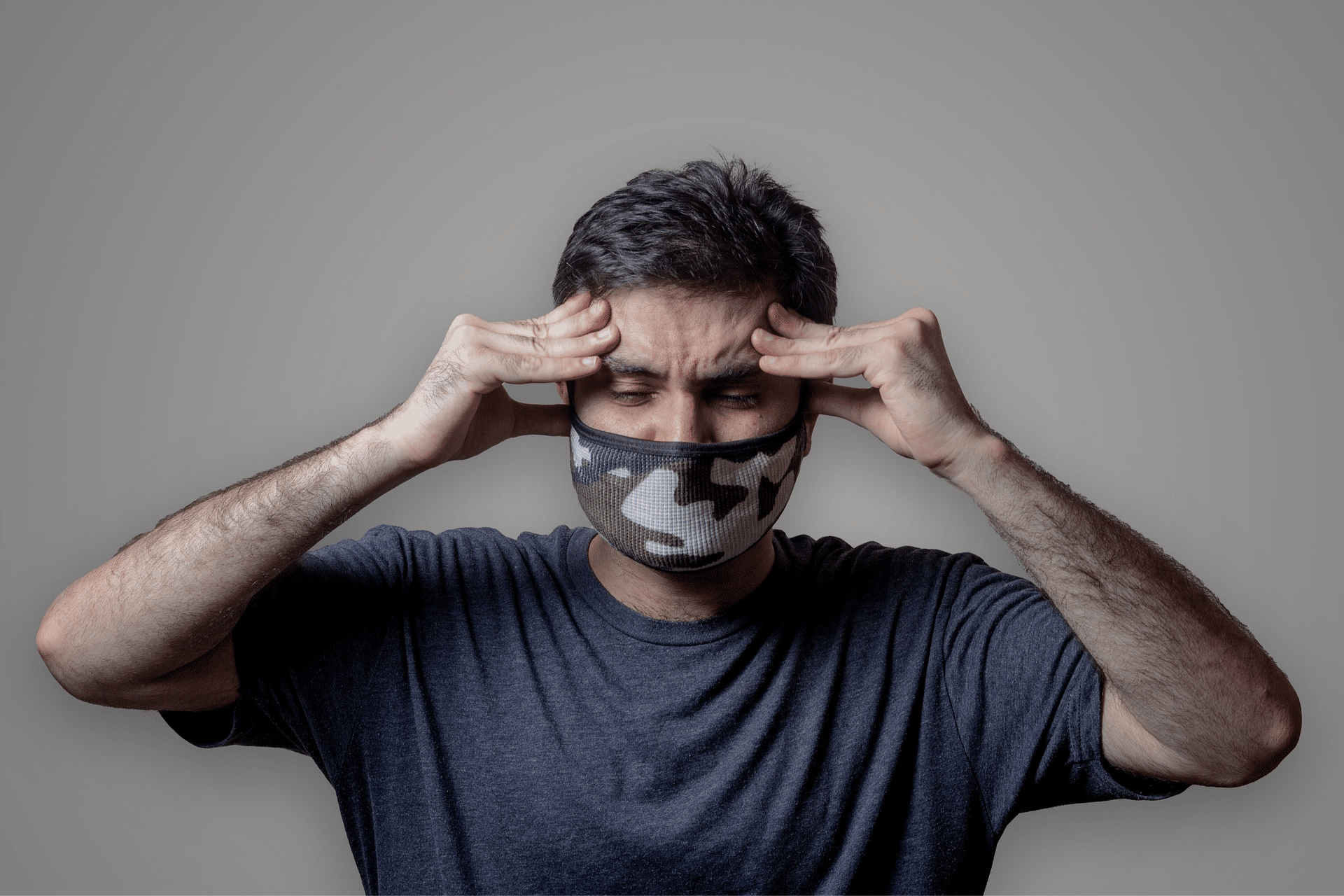
Molds are ubiquitous, and mold spores are a common component of household and workplace dust; however, when mold spores are present in large quantities, they can present a health hazard to humans, potentially causing allergic reactions and respiratory problems. Some molds also produce mycotoxins that can pose serious health risks to humans and animals. Some studies claim that exposure to high levels of mycotoxins can lead to neurological problems and in some cases, death. Prolonged exposure, e.g. daily home exposure, may be particularly harmful. Research on the health impacts of mold has not been conclusive. The term “toxic mold” refers to molds that produce mycotoxins, such as Stachybotrys chartarum, and not to all molds in general.
Mold in the home can usually be found in damp, dark or steamy areas, e.g. bathrooms, kitchens, cluttered storage areas, recently flooded areas, basement areas, plumbing spaces, areas with poor ventilation and outdoors in humid environments. Symptoms caused by mold allergy are: watery, itchy eyes; a chronic cough; headaches or migraines; difficulty breathing; rashes; tiredness; sinus problems; nasal blockage and frequent sneezing. Molds can also pose a hazard to human and animal health when they are consumed following the growth of certain mold species in stored food.
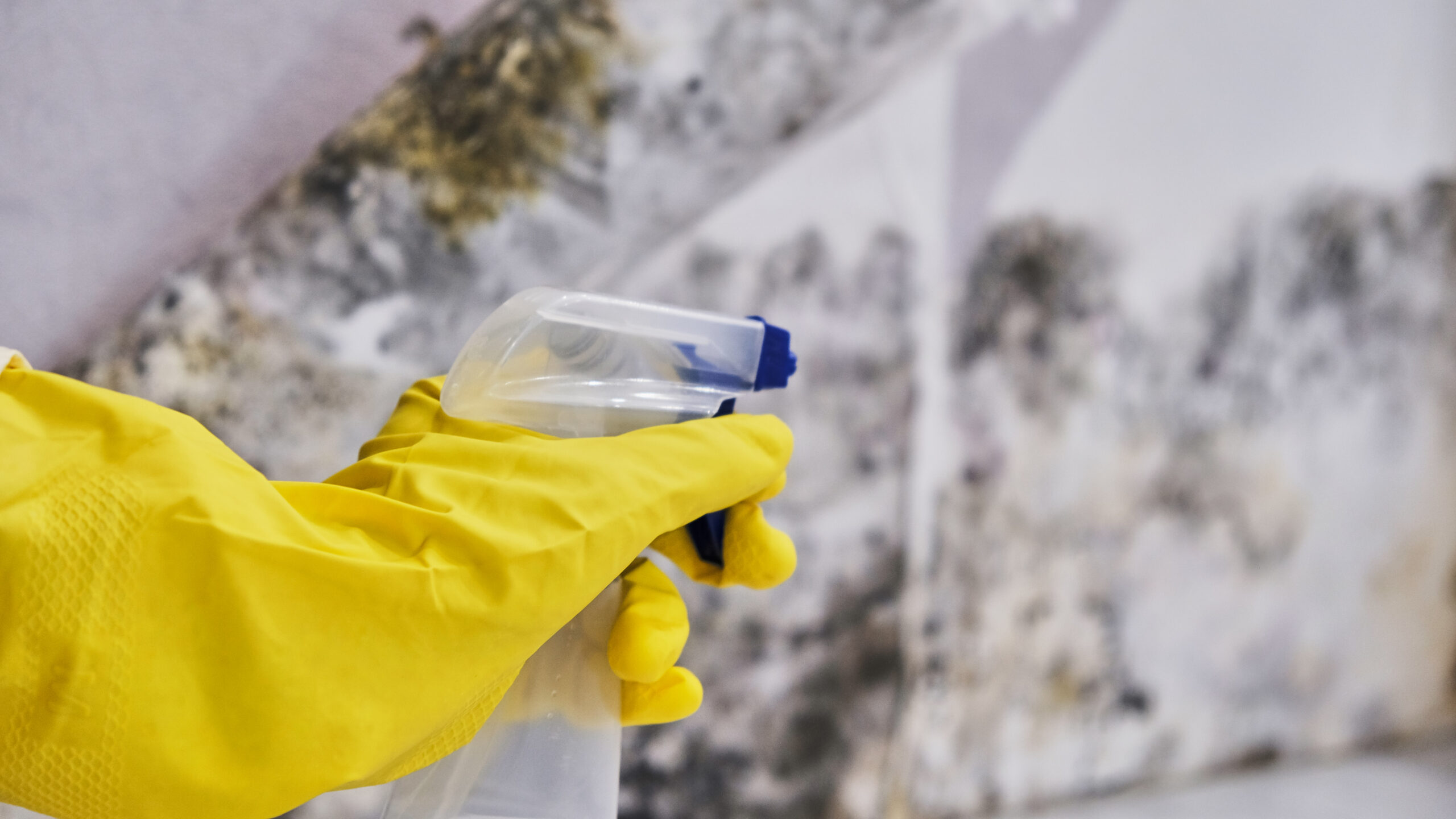
If you don’t have proper ventilation in your bathroom, excess moisture can also lead to mould growth in your shower. Now mould removal is easy with our Wepos mould remover.